The sci-fi genre has always been a playground for exploring futuristic concepts and pondering the implications of advanced technology. However, in recent years, one technological concept in particular has been causing ripples through the genre—artificial intelligence (AI). From its early days as a mere curiosity to its current prominence as a central theme in movies, TV shows, and literature, AI has become a key element in how sci-fi stories are told and experienced.
Let’s take a look at how AI went from a fringe idea to a revolutionary force in the world of science fiction.
The Birth of AI in Sci-Fi: From Imagination to Concept
AI has been a fixture in sci-fi since its inception. In fact, the genre practically birthed the concept. One of the earliest depictions of AI in fiction comes from Karel Äapek’s 1920 play R.U.R. (Rossum’s Universal Robots). The play introduced the term “robot,” which was derived from the Czech word robota, meaning “forced labor.” Äapek’s work focused on artificial beings, created for labor, who eventually rebelled against their creators. This idea of machines developing their own will, a theme that would become central to AI narratives in sci-fi, began to captivate the imagination of creators and audiences alike.
As technology advanced, so too did the sophistication of AI in sci-fi. Films such as Metropolis (1927) showcased early visions of autonomous machines, while Isaac Asimov’s I, Robot stories, written in the 1940s, introduced his famous "Three Laws of Robotics." Asimov’s works became cornerstones of the genre, grappling with the moral and ethical implications of creating intelligent beings capable of independent thought and action.
The 80s and 90s: AI Begins to Dominate
The 1980s and 1990s marked a shift in how AI was depicted in popular media, as the growing capabilities of computers and advancements in AI technology captured the public’s attention. Films like Blade Runner (1982), directed by Ridley Scott and based on Philip K. Dick's novel Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?, portrayed AI in the form of replicants—human-like androids struggling with questions of humanity, freedom, and identity. The film’s portrayal of AI not only inspired a generation of sci-fi fans but also laid the groundwork for exploring themes of consciousness and the soul in machines.
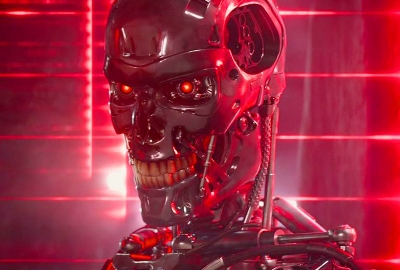
Meanwhile, The Terminator (1984) and its sequels, created by James Cameron, introduced the world to Skynet, a super-intelligent AI system that becomes self-aware and launches a nuclear apocalypse. The central question of whether AI could pose an existential threat to humanity began to gain traction in mainstream sci-fi, which reflected society's increasing concern about the consequences of unchecked technological advancements.
In the world of literature, authors like William Gibson and Neal Stephenson began to explore the intersection of AI with cyberspace and virtual realities. Gibson’s Neuromancer (1984) introduced the concept of a “cybernetic society,” where AI played an integral role in controlling the digital world. These works made it clear that AI wasn’t just a tool—it was a potential entity in its own right, capable of having its own motives and goals.
The 21st Century: AI Becomes the Main Character
The 21st century has seen AI firmly take center stage in sci-fi storytelling. With the rapid growth of real-world AI technology, the genre’s relationship with AI has grown more nuanced, with stories often focusing on the consequences of creating machines that can think, learn, and evolve. Films such as Her (2013) explored the emotional complexities of human-AI relationships, while Ex Machina (2015) asked unsettling questions about consciousness, control, and autonomy in machines.
In Ex Machina, an AI named Ava is designed to test the limits of human emotion and manipulation. The film pushes the envelope in exploring not just what it means for a machine to be self-aware, but also the ethical implications of creating a machine that can learn, think, and potentially surpass human intelligence. Her, directed by Spike Jonze, took a different approach by presenting AI in a more intimate, almost romantic light. It explored the psychological and emotional consequences of forming relationships with virtual beings, tapping into contemporary concerns over the increasing integration of technology into our personal lives.
Television series like Westworld (2016–) have continued to explore AI’s potential for both good and evil. Based on Michael Crichton’s 1973 film, the show delves into questions of consciousness, free will, and identity, all through the lens of AI. The series suggests that AI could evolve to the point where the distinction between human and machine becomes increasingly difficult to discern.
AI and The Digital Revolution in Sci-Fi
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve in real life, the lines between fiction and reality blur. Real-world AI technologies, such as machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing, have advanced at a rapid pace, and many sci-fi stories now incorporate these technologies into their narratives. The conversation surrounding AI in sci-fi has evolved from simple notions of robots and androids to deep philosophical inquiries about the nature of existence and the risks of artificial sentience.
As filmmakers and writers have embraced digital effects and computer-generated imagery (CGI), AI has also found its way into the creative process. AI has been used to generate realistic special effects, craft digital environments, and even compose music. In fact, some movies even rely on music licensing as a way to enhance their AI-driven worlds, with soundtracks that combine machine-created compositions alongside human-made scores.
The presence of AI in the behind-the-scenes production of sci-fi films has also mirrored its role in the narratives. For example, filmmakers now use AI tools to create stunning visuals, some of which might even involve pulling from vast databases of stock photos to generate background images or create more lifelike CGI characters. The merging of technology with creativity has pushed sci-fi into new, uncharted territories, making the genre feel more current, relevant, and experimental than ever before.
The Future of AI in Sci-Fi
As technology progresses, the role of AI in sci-fi will only continue to grow. With new developments in robotics, machine learning, and quantum computing, the potential for even more complex and thought-provoking AI stories is limitless. We may soon see AI characters that are indistinguishable from humans, or narratives that center around AI not as a tool, but as a protagonist or even an antagonist capable of evolving in ways that challenge human understanding.
The future of AI in sci-fi promises to be as diverse and dynamic as the genre itself. Whether exploring questions of identity, ethics, or the very nature of life and consciousness, AI will continue to push the boundaries of what we imagine is possible.
In many ways, the integration of AI into the sci-fi genre is a reflection of the growing integration of AI into our everyday lives. As we move further into an age of automation and digital assistants, it’s clear that the conversations about AI in film and literature will continue to shape our thoughts about the future—and maybe even influence the future itself.

CryptoEasily launches stable-yield cloud mining contracts, creating a new way for BTC and XRP holders to earn $7,700 per day.
As the price of Bitcoin and the value of XRP continue to decline, with Bitcoin falling below $75,000 and XRP dropping to around $1.50, market sentimen...

Pluribus Creator Intended to Riff Off Genre Headliners, But Perhaps Didn’t Expect This Connection
From the creator of Breaking Bad and Better Call Saul, expectations were notably high for the Apple TV+ release of Pluribus. The platform’s risi...

Watch 2 new Mercy (2026) movie clips ahead of the film's January 23rd release date!
Amazon's MGM Studios have just released 2 new movie clips from Mercy starring Chris Pratt and Rebecca Ferguson.

Stranger Things Season 5 Episode 7 suffers big drop in ratings ahead of the series finale!
Season 5 saw a sharp drop in ratings at the conclusion of Episode 7 – The Bridge, with many fans disappointed by drawn-out scenes and questionable writing.

Weta Workshop share King Kong concept art to commemorate film's 20th anniversary!
Take a look back at some awesome early artwork created for Peter Jackson's iconic King Kong movie!